Sample information |
|
| Picture |

|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Collection date | 11/14/2024 |
| Captive / Cultivated? | Wild-caught |
| Group | Hawaii Community College |
| Observations | Red Fire Ants are pretty small so this did concern me if the DNA would be effectively amplified to be shown in the end results. But it’s size and body structure made DNA extraction fairly easy. |
| Putative identification | Arthropoda |
Methods |
|
| Extraction kit | pcr |
| DNA extraction location | Whole arthropod |
| Single or Duplex PCR | Single Reaction |
| Gel electrophoresis system | Standard electrophoresis system |
| Buffer | TBE |
| DNA stain | SYBR Safe |
| Gel images |

|
| Protocol notes | Gel Lanes:
Positive and negative controls are not shown, but they both worked. Experimental Set Up
|
Results |
|
| Wolbachia presence | Yes |
| Confidence level | High |
| Explanation of confidence level | My results indicated that Wolbachia was present because the results from gel electrophoresis showed bands with the corresponding size. Rows three and four of the Wolbachia DNA had clear bands indicating it was found. When comparing my data to my control group they looked similar so I am confident it was successful that Wolbachia was found in both Red Fire Ants. |
| Wolbachia 16S sequence | Download AB1
|
| Arthropod COI sequence | Download AB1
|
| Summary | The Arthropoda was found to be postive for Wolbachia. |
 Ant like creature – Draft
Ant like creature – Draft Myrmaplata plantaleoides (Unsure) – Draft
Myrmaplata plantaleoides (Unsure) – Draft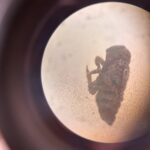 leaf hopper nymph
leaf hopper nymph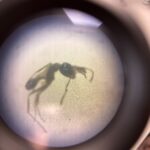 Pheidole species (Minor Worker)
Pheidole species (Minor Worker) JTR 1
JTR 1