Sample information |
|
| Picture |


|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Collection date | 11/01/2023 |
| Captive / Cultivated? | Wild-caught |
| Group | John Overton High School |
| Observations | Most of the insects collected, specifically beetles, were found under logs; so, dark, small, and hidden places. |
| Putative identification | Arthropoda Insecta Coleoptera |
Methods |
|
| Extraction kit | DNeasy (Qiagen) |
| DNA extraction location | Abdomen |
| Single or Duplex PCR | Duplex Reaction |
| Gel electrophoresis system | Standard electrophoresis system |
| Buffer | TAE |
| DNA stain | SYBR Safe |
| Gel images |

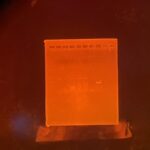
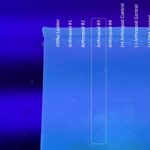
|
| Protocol notes | DNA Extraction: I took great care to thoroughly crush the arthropod, as well as removing the abdomen, leaving the exoskeleton behind. Gel Electrophoresis Lanes for CO1 arthropod PCR:
|
Results |
|
| Wolbachia presence | No |
| Confidence level | Medium |
| Explanation of confidence level | After receiving the results from the samples collected and tested, the bands for my collected sample, Arthropod #3, weren’t visible for Wolbachia. On the other hand, the bands for Arthropod #4 and the (+) Arthropod Control were both visible for Wolbachia. The controls did show signs of success, still, I’d rather consult with scientists who were present before I come to a solid conclusion. |
| Wolbachia 16S sequence | |
| Arthropod COI sequence |
|
| Summary | The Coleoptera was found to be negative for Wolbachia. |
 Ant like creature – Draft
Ant like creature – Draft Myrmaplata plantaleoides (Unsure) – Draft
Myrmaplata plantaleoides (Unsure) – Draft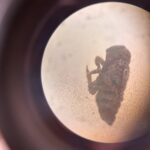 leaf hopper nymph
leaf hopper nymph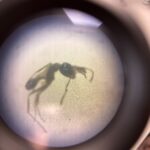 Pheidole species (Minor Worker)
Pheidole species (Minor Worker) JTR 1
JTR 1