Sample information |
|
| Picture |

|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Collection date | 06/07/2023 |
| Captive / Cultivated? | Wild-caught |
| Group | Pingry School |
| Observations | We found the bug sitting on the edge of a log. The bug was very well camouflaged and looked exactly like a living leaf. While dissecting the bug, we saw a blue-like substance inside the abdomen which we couldn’t identify. |
| Putative identification | Arthropoda Insecta Hemiptera |
Methods |
|
| Extraction kit | DNeasy (Qiagen) blood and tissue kit |
| DNA extraction location | Whole arthropod |
| Single or Duplex PCR | Single Reaction |
| Gel electrophoresis system | Standard electrophoresis system |
| Buffer | TAE |
| DNA stain | SYBR Safe |
| Gel images |
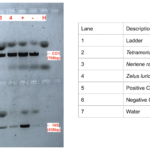
|
| Protocol notes | The sample extracted from the Pale Green Assassin Bug is in lane 4. The top half of the gel shows results for the CO1 gene, and the bottom half shows results for the 16S gene. We prepped the samples and then ran them through a gel for approximately 20 minutes at 100v. We then ran the gel for approximately 15 minutes at 10v while waiting to view results. The sample in Lane 4 (Pale Green Assassin Bug) had a band that lined up with the band from the + arthropod control, meaning our putative insect had a positive band at the CO1 arthropod gene. The sample in lane 4 (Pale Green Assassin Bug) also had a band that lined with the expected + Wolbachia control band, meaning the insect had the 16S gene and Wolbachia infection. |
Results |
|
| Wolbachia presence | Yes |
| Confidence level | High |
| Explanation of confidence level | The band in lane 4 (Pale Green Assassin Bug) that lined up with the + arthropod control was very dark and thick. Furthermore, the band that lined up with the + Wolbachia control was very visible. We further went on to test the DNA concentration of the CO1 and 16S samples of the Pale Green Assassin Bug in a Nanodrop, and found the concentrations to be 16.2ng/uL and 7.9ng/uL respectively, meaning the samples had DNA. |
| Wolbachia 16S sequence | Download FASTA
Download AB1
TAAGCCTGCCGACTTATCAGCCCAGTGAAGACACCATGGTAGCAAGTGTGTAGCGCACTCTCCAAAGAGCATGATGATGTGATATAATTACCAGCTCCTAANATTGAACATAGGCAGTTTCCTTGTGTTGAGAGCATTGCCCGATGGCCACTGGGGCCTCCGGTTGCGCTGGNTGCGGGACTTAGCGGGGCAGCTCATGCANCAGCTTACTACCCCTCTGTCGCCAATTCGTCTAGTCCGTCCGCACCGTGCGTATTCGTTNGAATAGGTCTGANACTTTTTTTGTTATTTCTTTANTANGG
BLAST at The Wolbachia Project BLAST at NCBI
|
| Arthropod COI sequence | Download FASTA
Download AB1
TGGATCACCTCCCCCAGATGGGTCAAAGAATGAAGTATTAAAGTTTCGATCAGTTAATAGCATAGTAATAGCCCCTGCTAAAACAGGAAGAGATAATAATAAAAGTAATGCAGTAATTCCTACTGATCAGACAAATAATGGGATTCGTTCAGGAGTTATTCCAGCAGGTCGTATATTAATAATTGTTGAAATAAAATTAACTGCTCCTAAGATTGAAGATACTCCGGCTAAGTGTAATGAGAAAATTGCTAAATCTACAGCTGCACCTCTATGAGCTATATTACTAGATAAGGGGGGATAAACAGTCCATCCTGTTCCTGCCCCTCCTTCAGCAATTCTTCTAATTAATAACAAGGTTAGGGAAGGGGGAAGAAGTCAAAATCTTATATTATTTATTCGGGGGAAGGCTATATCAGGAGCTCCAATTATAAGGGGTACTAATCAATTCCCAAATCCTCCAATTATAATAGGCATAACTATAAAGAAAATCATAATAAATGCGTGTGCAGTAACGAATACATTATAAATTTGATCATTTCCAATAAAAGTACCTGGAGTACCTAATTCAATTCGAATTATTCATCTTAAGGAGGTTCCAATAACCCCTGCTCAAGCACCTAGCAGAAAATATAGAGTTCCAATATCTAT
BLAST at The Wolbachia Project BLAST at NCBI
|
| Summary | The Hemiptera was found to be postive for Wolbachia. |
 Ant like creature – Draft
Ant like creature – Draft Myrmaplata plantaleoides (Unsure) – Draft
Myrmaplata plantaleoides (Unsure) – Draft leaf hopper nymph
leaf hopper nymph Pheidole species (Minor Worker)
Pheidole species (Minor Worker) JTR 1
JTR 1